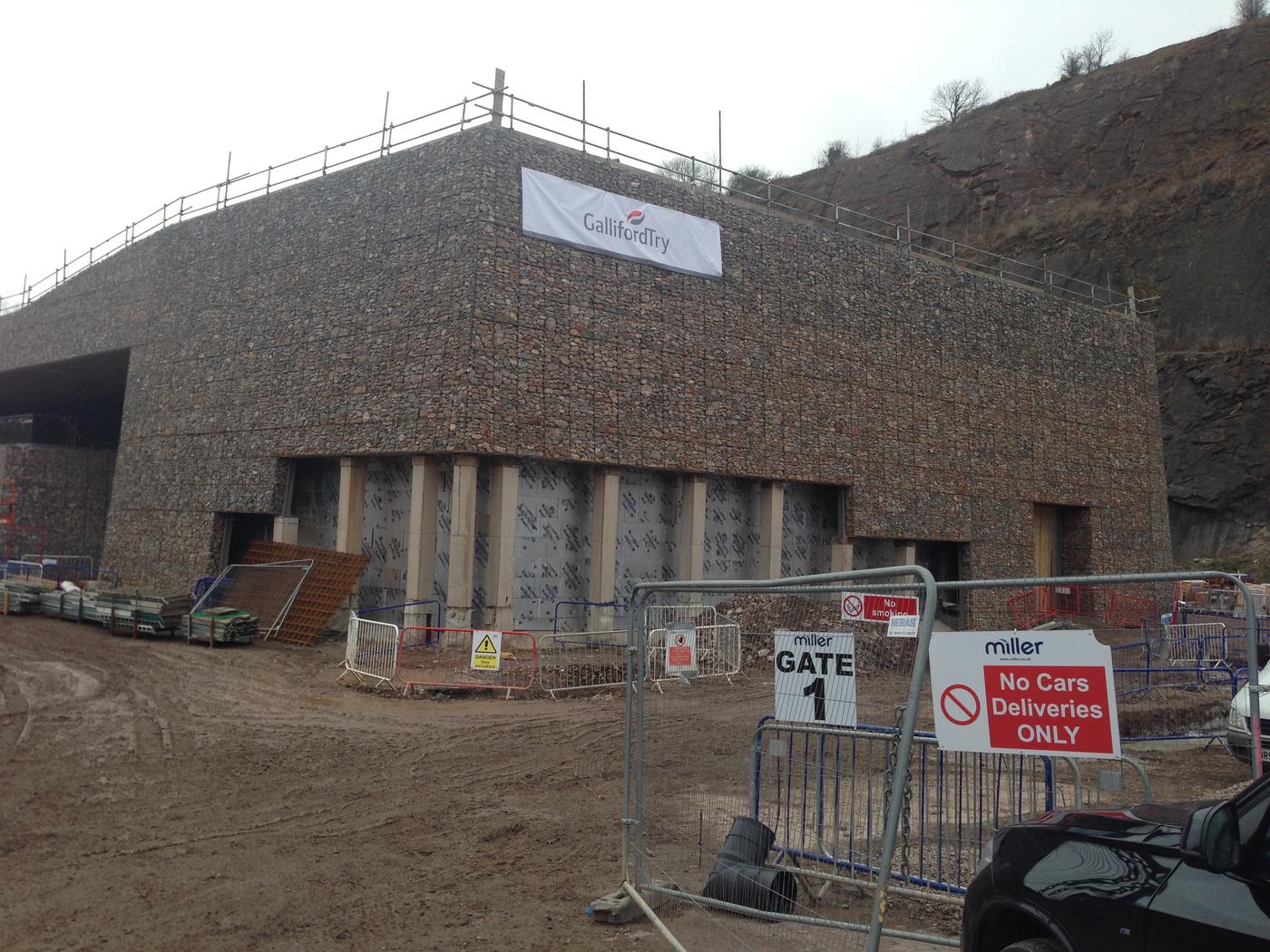
Due to their architectural appearance, gabions can be used to clad buildings or retaining walls that are not aesthetically pleasing, such as sheet piled walls. Typically thinner than a normal gabion wall would be, this method of cladding is very effective and becoming more popular. Free standing gabion walls can also be used as environmental or visual screens.
Common uses
Process
Gabion cladding is made using welded mesh that is ridged and easier to work with. There are various methods for attaching gabion cladding to buildings. Steel frames, or fixings can be used to attach ether rear gabion mesh panel. Then diaphragms and a front panel are used to create a void which will then be filled with stone. The panels are usually 150-200mm thick, which allows hand placement of stone for an architectural finish.
Free standing gabion walls are typically thinner that standard gabion walls, but will have support columns within the structure to give added strength.

